Polyurethane
Polyurethane (EU/AU)
Polyurethanes are noted for outstanding resistance to abrasion and tear. Polyurethanes provide the highest available tensile strength among all elastomers while providing good elongation characteristics. Ozone, oxidation, sunlight, weather, oil and incidental gasoline exposure are environments suited for urethane applications. Polyether based polyurethanes (EU) are directed toward low temperature flexibility applications. The polyester based polyurethanes (AU) provide improved abrasion, heat and oil swell resistance.
Polyurethanes are not recommended for alkalis, acids and oxygenated solvents. Polyester based polyurethanes are not typically recommended for hot water, steam and high humidity applications, but can be formulated to improve resistance to these properties.
Compounds 522GN, 522MD, 522FX, 522NR
- Superior tensile strength compounds
- Excellent abrasion resistance
- Low temperature operation to -40°F (-40°C)
Compounds 512AC
- Excellent tensile and elongation properties
- Low temperature properties to -70°F (-57°C)
| Compound | Hardness Shore A | Tensile MPa | Tensile psi | Elongation (%) | Oil Aging Volume Swell (Change %) 70hr at 100°C/212°F ASTM #1 | Oil Aging Volume Swell (Change %) 70hr at 100°C/212°F IRM 903 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 522GN | 60 | 18.1 | 2530 | 670 | -11 | -7 |
| 522MD | 75 | 22.8 | 3300 | 280 | -3 | +4 |
| 522FX | 70 | 24.8 | 3600 | 320 | -2 | +4 |
| 522NR | 90 | 23.4 | 3400 | 125 | +4 | +0 |
| 512AC | 80 | 26.2 | 3800 | 430 | -5 | +14 |
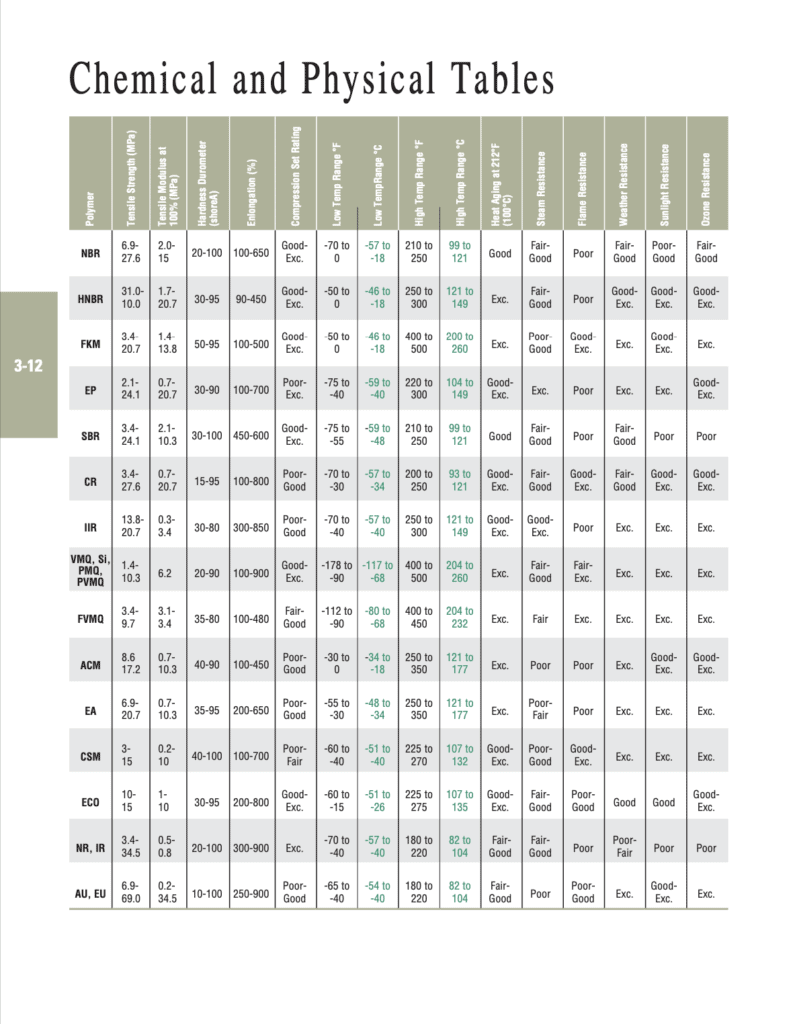
Chemical and Physical Tables
Click below to view the Elastomers/Materials: Chemical and Physical Tables PDF